You may have confidential data on your hard drive in spaces where data may have been stored temporarily.
You may also have deleted files by using the Windows Recycle Bin and then emptying it. While you are still using your local hard drive, there may be confidential information available in these unoccupied spaces.
Wiping the logical drive's deleted data does not delete existing files and folders. It processes all unoccupied drive space so that recovery of previously deleted files becomes impossible.
Installed applications and existing data are not touched by this process. When you wipe unoccupied drive space, the process is run from the bootable CD/DVD operating system. As a result, the wipe or erase process uses an operating system that is outside the local hard drive and is not impeded by Windows system caching. This means that deleted Windows system records can be wiped clean.
KillDisk wipes unused data residue from file slack space, unused sectors, and unused space in MFT records or directory records.
Wiping drive space can take a long time, so do this when the system is not being otherwise utilized. For example, this can be done overnight.
The process of deleting files does not eliminate them from the hard drive. Unwanted information may still be left available for recovery on the computer. A majority of software that advertises itself as performing reliable deletions simply wipes out free clusters. Deleted information may be kept in additional areas of a drive. KillDisk therefore offers extra steps to ensure secure deletion.
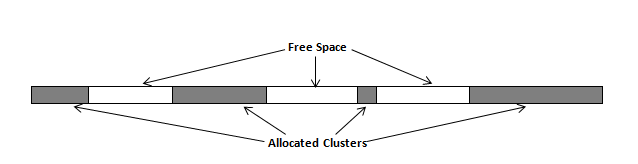
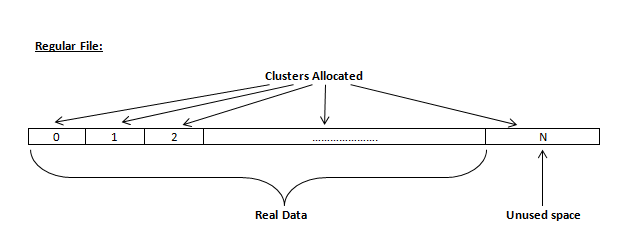
This relates to any regular files located on any file system. Free space to be wiped is found in the "tail" end of a file because disk space is usually allocated in 4 KB clusters. Most files have sizes that are not 4KB increments and thus have slack space at their end.
|
This document is available in PDF format, which requires Adobe® Acrobat® Reader
|